Causes of Jaw Pain
There are many causes of jaw pain.
Those that cause pain on either one side or both sides of the jaw are:
-
TMJ Disorders
It is the most common cause of jaw pain, and it is more common among women.
Signs and symptoms include pain or tenderness in the jaw, pain in one or both TMJs, clicking sound upon opening of the mouth, difficulty chewing or pain while chewing, pain around the ears, headache, ringing in the ears, dizziness, and vision problems.
Risk factors for TMJ disorders include teeth grinding at night, involuntary clenching of the jaw due to stress and anxiety, and trauma to the jaw joint. (4, 5)
-
Trauma
Trauma to the jawbones, such as fractures and dislocations, can also cause jaw pain. (6)
-
Dental Problems
Dental problems such as gum disease, cavities, and tooth infection (abscess) can cause pain that radiates to the jaw. (4)
-
Sinus problems
The sinuses are air-filled nasal cavities. Sinus infection can lead to overproduction of mucus, which puts pressure on the jaw, causing pain. (4)
-
Arthritis
Some kinds of arthritic conditions, such as osteoarthritis, can affect the TMJ, which leads to pain and a stiffer TMJ. (3, 6)
-
Giant cell arteritis
Giant cell arteritis is an inflammatory disease of the blood vessels. Signs and symptoms include fever, headache, pain over the temples, double vision, and pain in the jaw while chewing. It is more common in women than men, and it usually occurs after the age of 55. (3, 7)
-
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is infection of the bone. Osteomyelitis can affect the jawbones, leading to jaw pain. (3, 6)
Those that cause pain on only one side of the jaw, either left or right, are:
-
Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches typically cause pain behind or around one of the eyes, but the pain can radiate to the jaw. Cluster headaches are one of the most painful types of headache. (3, 4)
-
Trigeminal neuralgia
This is a condition in which the nerves to the face are compressed or damaged, resulting in severe pain in one side of the face, including the jaw. (3, 4)
The condition that typically causes pain on the left side of the jaw is:
-
Heart attack
Heart attack can cause pain in other areas aside from the chest, such as the left side of the jaw and face, neck, left arm, and back. Women are more likely to experience jaw pain during heart attack. It can be accompanied by signs and symptoms such as chest discomfort, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and faintness. (4)
Jaw Anatomy and Pictures
The jaw consists of the upper jaw and the lower jaw.
The upper jawbone is called the maxilla. It includes the frontal portion of the palate. (1)
The lower jawbone is also called the mandible. It is the largest, strongest, and lowest bone in the human face. It connects to the skull at a pair of joints known as the temporomandibular joints (TMJs). The jawbone is the only movable bone of the skull, aside from the small bones in the middle ear. (2)
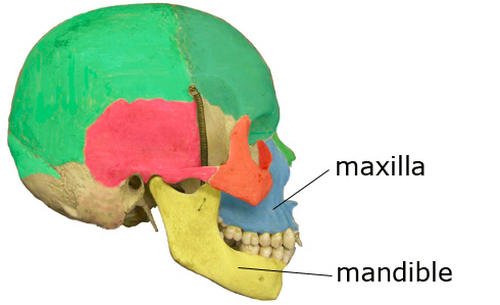
Image 1: The human skull with emphasis on the upper and lower jaws.
Picture Source: inside.ucumberlands.edu
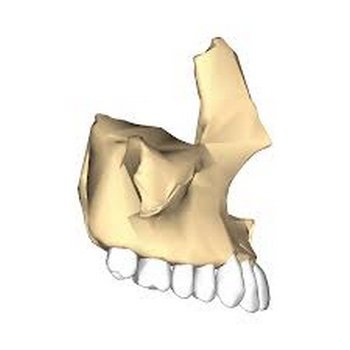
Picture 2: The upper jawbone holding the upper set of teeth.
Photo Source: encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
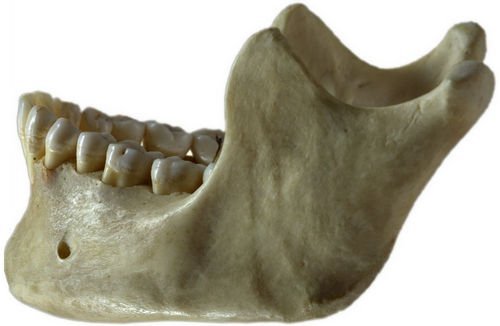
Photo 3: The jawbone holding the lower set of teeth.
Image Source: upload.wikimedia.org
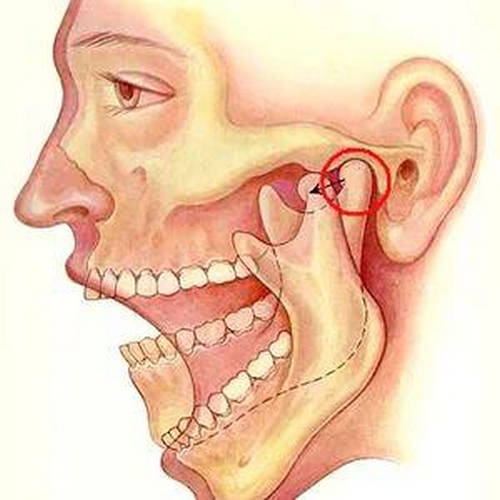
Image 4: The TMJ (encircled), allowing the mouth to open and close.
Picture Source: pimg.39.net
Jaw Function
The upper jawbone holds the upper set of teeth and gums, while the lower jawbone holds the lower set of teeth and gums. The lower jawbone also allows opening and closing of the mouth around the TMJ. (1, 2)
Signs and Symptoms of Jaw Pain
Aside from jaw pain, other accompanying signs and symptoms include:
- facial pain that worsens when the jaw is moved
- joint and muscle tenderness
- limited range of motion
- jaw alignment problems
- clicking sounds with opening or closing of the jaw
- ringing in the ears
- pain in or around the ear
- headaches with or without ear pain and pressure behind the eyes
- dizziness
- vertigo
- locking of the jaw
- dull aching to sharp stabbing pain
- becoming overly sensitive to pain
- toothache
- neuropathic pain
- fever
Signs and symptoms depend on the cause. It is important to seek prompt medical care in order to correctly diagnose the disease that causes jaw pain. (3)
Treatment of Jaw Pain
Treatment varies depending on the cause of jaw pain. Some treatments include:
- Soft diet – to avoid excessive jaw movement and crunching
- Ice packs or hot packs – to relax muscles and relieve pain
- Massage on the affected muscles – to relax muscles
- Pain medications – to relieve pain
- Mouth guard – to prevent teeth grinding at night
- Antibiotics – if eliminate infection
- Physical therapy – to relax muscles and increase range of motion of TMJ
- Muscle relaxants – to relax affected muscles
- Botox injections – to relax affected muscles
- Relaxation therapy and stress avoidance – to relieve tension on muscles
- Steroids – to reduce inflammation
- Root canal treatment – to treat tooth infections
- Surgery – to remove damaged bone, treat affect nerve, or to correct structural problems (3, 4, 8)
Prevention of Jaw Pain
Knowing the cause of jaw pain is important to prevent recurrence. Some preventive methods include:
- Eating soft food and avoiding crunchy food
- Avoiding teeth grinding
- Reducing stress
- Regularly seeking dental care
- Having proper posture
- Avoiding caffeine, which contributes to muscle tension (3)
When to see the doctor
Consult your doctor when the following conditions occur:
- Failure of home remedies such as cold or hot packs, over-the-counter pain medications, massage)
- Inability to eat or drink
- Jaw pain that interferes with daily living
- Jaw pain that interferes with sleep
- Presence of chest discomfort, difficulty of breathing, sweating, nausea and faintness because the cause could be heart attack
- Presence of headache, eye pain, ear pain, ringing in the ears, dizziness, or vision problems
- Irregular jaw motion or locking of the jaw
- Dental problems such as abscess and gum disease (3, 8)
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maxilla
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mandible
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317184.php
- https://www.healthline.com/health/jaw-pain#causes
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/why-your-jaw-hurts#1-3
- https://www.medicinenet.com/jaw_pain/symptoms.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Giant-cell_arteritis
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/temporomandibular-disorder-tmd/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tmj/symptoms-causes/syc-20350941
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trigeminal_neuralgia#Signs_and_symptoms