Spleen pain/ splenic pain is mainly referred to, as and when a left upper quadrant pain in the abdomen is felt. This is because the spleen is located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
What is Spleen?
It is a lymphoid organ which is almost the size of a fist and helps in immunity of the body. [1] The location of spleen in the body protects it from outside trauma.
It is an organ of the abdomen that is situated on the left side below the lower ribs and behind the stomach. Because of its deep position, it generally does not get injured easily.
A blunt trauma to the abdomen due to accident or any other cause can rupture the spleen.
Where is your spleen located?
Spleen lies in the left upper quadrant of abdomen, covered by the 9th, 10th and 11th ribs of the left side and upper part of stomach in front, and the upper part of left kidney behind. The tail of pancreas is attached to the hilum of the spleen.
When examined by a doctor, it cannot be felt under normal conditions. When it is enlarged, it can be felt at the lower end of the rib cage, in front.
Anatomy : Spleen Location and Pain location

Picture 1: Spleen location
The image shows spleen’s location inside the abdomen and how it looks.
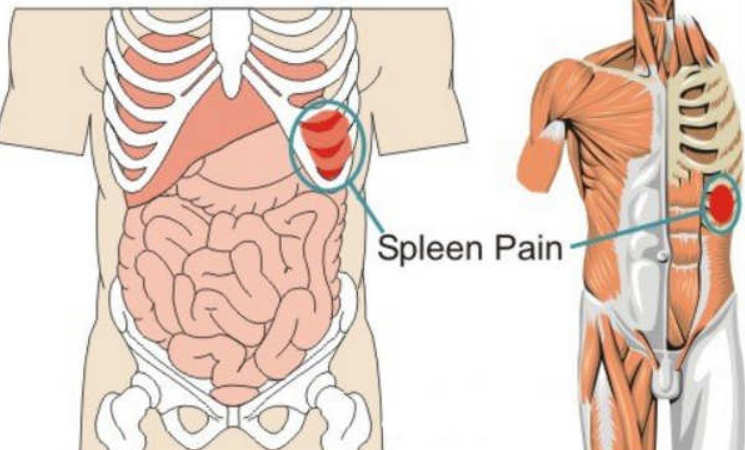
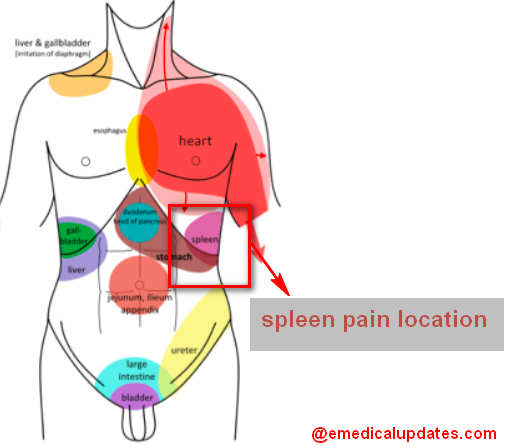
Picture 2 and 3 : Spleen pain location
What does the spleen do ? Function
Spleen is known to have lots of functions especially in regards to immunity and helping in keeping the blood clean by acting as a filter.
- Largest lymphoid organ in the body [2]. When blood passes through it, bacteria, viruses, parasites and foreign bodies are caught within the splenic sinusoids and removed.
- Synthesis & Activation of lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes produce antibodies that fight against various infective antigens.[3, 4]
- Removal of RBC. The RBCs after completing their life span of about 120 days are removed by spleen. [4]
- Acts as a reservoir of blood. [4]
- In the foetal life, spleen produces RBCs too. [5]
Can you live without a Spleen?
Yes. We remove the spleen surgically in certain conditions such as rupture of the spleen, tumour, sickle cell anemia etc. [10]
Living without a spleen is more of a fight against various infections. Asplenic people are more prone to infections with bacteria which are having capsule (Capsulated). Eg: Hemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae etc. [11]
Causes of Left Upper Quadrant Pain
The left upper quadrant pain can be due to trauma, infection, inflammation, perforation, malignancy etc. Diagnosing the exact cause is very important for its further management. The pain in the region may arise from the organs present in the area, that is, spleen, intestine, kidney and pancreas.
| Condition | Clinical features | Diagnostics |
| Splenic trauma/Infarct |
|
|
| Splenomegaly (Enlarged spleen) |
|
|
| Mesenteric Ischemia |
|
|
| Small Bowel Obstruction |
|
|
| Crohn’s disease |
|
|
| Mesenteric adenitis |
|
|
| Acute pancreatitis |
|
|
| Pancreatic cyst/ malignancy |
|
|
| Pyelonephritis |
|
|
|
Perinephric abscess |
|
|
| Nephrolithiasis |
|
|
Table: Differential diagnosis for left upper quadrant pain. [6, 7, 8, 9]
Causes of Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen)
An enlarged spleen can occur in [1]
- Infections- Bacterial, viral, parasitic
- Cancers- Leukaemia, lymphoma
- Abscess
Conditions of Spleen pain for Left Upper Quadrant Pain
We have seen the causes which can give rise to a left Upper quadrant pain. But, what problems in spleen can cause a left upper quadrant pain? The pain in the spleen can be referred to the left shoulder (Kehr’s sign)[12] which can increase in intensity during inspiration.
This is due to the irritation of phrenic nerve by blood near to the left side of diaphragm. A rupture of spleen can result in massive internal haemorrhage which can be potentially life-threatening. [1, 12]
- Splenomegaly
- Splenic abscess
- Splenic infarct
- Splenic rupture
Treatment
Splenomegaly (Enlarged spleen): The treatment of underlying cause is the first step in reducing the size of spleen. [13]
The size increase just means that the spleen is doing extra work to filter and clear the blood. In certain conditions like hereditary spherocytosis or lymphoma, splenectomy may be the preferred treatment.[13]
- Splenic abscess : Broad spectrum antibiotic treatment along with percutaneous drainage (if not contraindicated) of the abscess can be helpful in selected patients. [14] In rest of the cases, open drainage of the abscess or splenectomy might have to be done.[15]
- Splenic infarct : A non-complicated infarct does not require any intervention other than NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). In case the infarct is complicated by an abscess, sepsis, haemorrhage or persistent pseudocyst formation, surgical intervention maybe necessary. [16]
- Splenic rupture : Patients with unstable hemodynamic status will mostly have to undergo splenectomy. With continuous monitoring and hemodynamic stability, supportive treatment may only be required. [17]
References:
- https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/enlarged-spleen-causes-symptoms-and-treatments#1
- http://www.organsofthebody.com/spleen/
- Janeway’s Immunobiology 8th Edition. New York, NY: Garland Science.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spleen
- “Spleen: Information, Surgery and Functions”. Childrens Hospital of Pittsburgh – Chp.edu. 2010-11-17.
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. McGraw-Hill. 2015.
- McGee, S.. Evidence-based Physical Diagnosis. Saunders. 2007
- Am J Emerg Med. vol. 27. 2009. pp. 262-265
- http://www.clinicaladvisor.com/hospital-medicine/left-upper-quadrant-abdominal-pain/article/600936/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asplenia
- Brigden, M. L. (2001). 63 (3): 499–506, 508
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/image?imageKey=PC%2F106201&source=contentShare&csi=93c5805e-2d42-42e4-8e69-89f87d08c06d
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/206208-treatment
- Pediatr Surg Int. 2013. 29:787-90
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/194655-treatment#d10
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/193718-treatment
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/432823-treatment#d10

