What is Anasarca?
Definition : Anasarca is a medical condition in which the whole body swells up. This is due to accumulation of fluid in the extracellular space (1). In general, doctors call it in different names such as generalized edema, massive edema or dropsy (2).
The rapid gain of weight due to bloating of the body, the pain, the discomfort and the difficulty in doing even simple tasks makes life very uncomfortable to a lot of people suffering from anasarca.
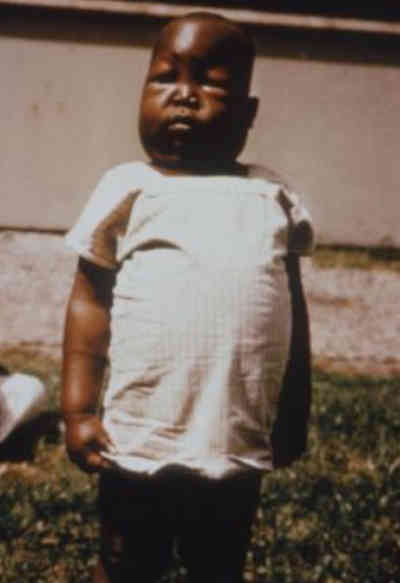
Picture 1: Image shows a child with anasarca due to nephrotic syndrome.
Photo Source: upload.wikimedia.org
Pathophysiology of Anasarca
To understand why there is a fluid accumulation in between the cells, we need to know the basics of our body hemodynamics(3, 4, 5, 6).
Blood flows through the vast network of blood vessels including arteries, veins, arterioles, venules and the capillaries. Blood though seen as fluid in nature, contains a lot of cells, proteins and other content dispersed in it.
The capillaries by nature are semipermeable and thus have minute openings which allow the fluid portion of blood (serum) to pass through into the space between the cells, outside the capillaries. If it were not for the hemodynamic forces which keep the fluid in its place, the whole world would be filled with bloated people.

Picture 2: A pictorial depiction of fluid distribution in the body. Intracellular fluid 40%, Interstitial fluid (IF) 15%, Plasma 5%. The picture also shows the shift of fluid from plasma to the interstitial space in case of edema.
Image Source: howshealth.com
The hemodynamic forces are as follows.
- The non-fluid content of the blood exerts an oncotic pressure which prevents fluid portion of the blood from flowing out through the capillaries.
- The hydrostatic pressure within the capillaries helps the blood to move forward. This also pushes the blood onto the capillary walls, which can result in small volume of fluid leaking out of the capillaries. But the balance between the oncotic pressure and the hydrostatic pressure prevents massive outflow.
- Sodium content in the interstitial space (space between the cells which are outside the capillaries) also determines the amount of fluid that remains there. When sodium is more in the interstitial space, there is more fluid retained there.
- Extra fluid in the interstitial space is removed by the lymphatic channel and carried ultimately back to the blood.
Any alteration in the above hemodynamics can result in the fluid collection within the interstitial space. The changes that causes localized edema or generalized edema (anasarca) are as follows.
- Decrease in oncotic pressure within the capillaries.
- Increase in hydrostatic pressure within the capillaries.
- Sodium and water retention by the kidneys.
- Blockage of the lymphatic channels.
- Increased permeability of the capillaries.
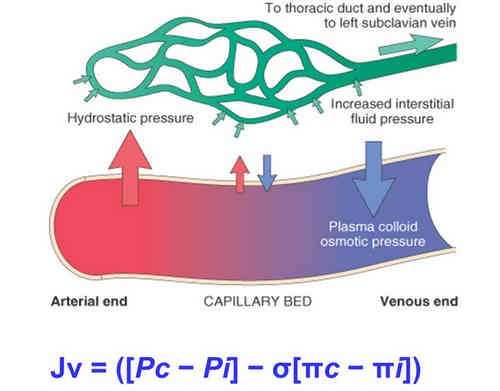
Picture 3: The picture shows normal hemodynamics at work in the blood vessels.
Photo Source : encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
Anasarca Causes
There are very many conditions that can lead to the above described pathophysiology and thus resulting in anasarca. The most common and important ones are given below.
Liver failure
Liver is an organ that produces many plasma proteins which helps in maintaining the oncotic pressure in blood vessels. When it fails, the proteins produced are less in amount and thus resulting in a decreased oncotic pressure.
Kidney failure
Kidney failure can lead to sodium and water retention and thus anasarca. Certain kidney diseases such as nephrotic syndrome can cause protein loss through the urine resulting in a decreased capillary oncotic pressure. (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13)
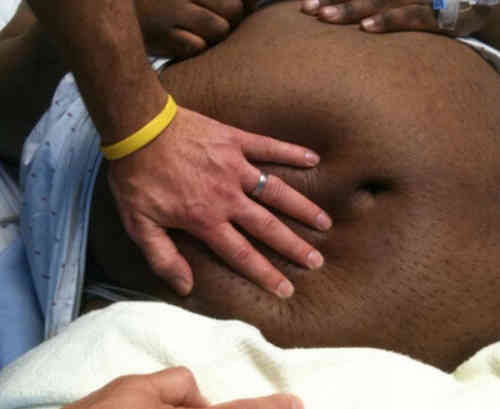
Picture 4: Ascites (Fluid retention in the abdomen) in a patient with renal failure.
Image Source: healthfixit.com
Congestive cardiac failure
The function of the heart is to pump blood. When it fails to pump effectively, the flow of blood slows down, resulting in the blood being held up in the veins before the right side of the heart. This means there is more blood in the veins of the limbs, abdomen and elsewhere. An increased hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries ensues.
Severe malnutrition
Protein energy malnutrition results in low protein in the circulation and thus a decreased capillary oncotic pressure.
Drugs
Certain drugs may cause sodium retention and thus edema.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
- Glucocorticoids
- Thiazolidinediones
- Insulins
- Estrogen, progestin, testosterone
Certain drugs may cause arteriolar vasodilation leading to edema.
- Vasodilators- Hydralazine, Minoxidil, Diazoxide
- Calcium channel blockers
- Methyldopa
Certain drugs may cause edema through unknown mechanisms
- Gabapentin, Pregabalin
- Docetaxel, Cisplatin
- Pramipexole, Ropinirole
- Chronic venous insufficiency – This increases the hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries.
- Increased capillary permeability – can be seen in burns, trauma and allergic reactions.
- Lymphatic obstruction – can occur due to malignancies and hypothyroidism.
- Hemoglobin Barts (Hb Barts)
- Hook worm infestation
- Pre-eclampsia
- Amyloidosis
- Polyneuropathy and monoclonal gammopathy syndrome
- Clarkson syndrome
Anasarca Signs and Symptoms
Swelling all over the body is the main feature of anasarca. Further, the patient may present with symptoms associated with the underlying cause(6, 7, 8, 9).
- Swelling of eyelids leading to difficulty in opening and closing of the eyes.
- Swollen face, lips and ear lobes may occur.
- Pitting edema shown by a depression on skin when pressure applied on the swellings.
- Variation in blood pressure and heart rates. They can either increase or decrease according to the cause of anasarca.
- Difficulty in breathing or chest pain can occur when there is pulmonary edema.
- Distended abdomen due to accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (Ascites)
- Swollen limbs
- Scrotal edema

Picture 5: Pitting edema in a child with anasarca.
Photo Source: encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
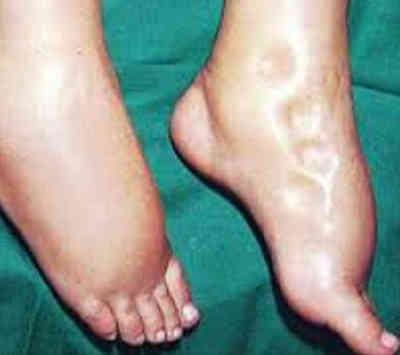
Picture 6: An adult with pitting edema demonstrated on the legs.
Image Source: healthncare.info
Diagnosis of Anasarca
Diagnosis of Anasarca requires a detailed clinical examination followed by appropriate investigations. The diagnostics may involve any or all of the following (6, 7, 8, 13).
- Urine analysis to check for protein loss
- Kidney function tests
- Liver function tests
- Chest X- ray
- Echocardiography
- Thyroid profile
- CT scan of chest and abdomen

Picture 7: A CT scan of patient with liver cirrhosis showing ascites.
Image Source: upload.wikimedia.org
Anasarca Differential diagnosis
Anasarca itself is a symptom of underlying serious condition. The differential diagnosis is the same as causes which are mentioned above. Kindly refer to the section for details.
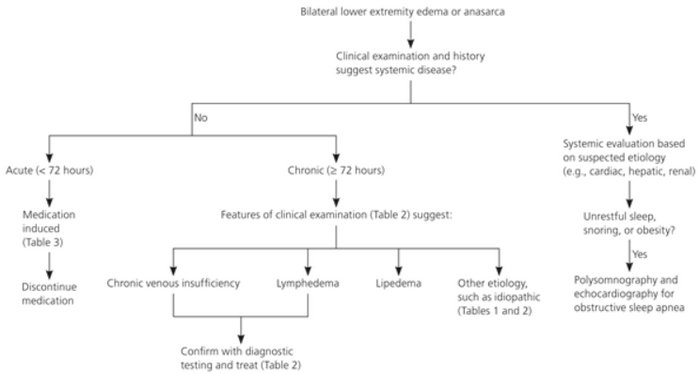
Picture 8: A flowchart showing the diagnostic sequence in case of anasarca.
Photo Source: www.aafp.org
Anasarca Treatment
Anasarca treatment guidelines are based on the diagnosis of cause. A multidimensional approach may be required to treat the condition. This may include
- Salt intake restriction
- Fluid intake restriction
- Adequate rest with lower limbs elevated
- Compression stockings
- Diuretic drugs
- Hemodialysis
- Fluid and electrolyte replacement in case of burns
- Thyroid hormone replacement in hypothyroidism
- Stopping of drugs leading to anasarca(13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18).
Reference:
- Kumar. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 8th ed. p.112; Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2010
- medinfo.org/anasarca-symptoms-causes-treatment-definition
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3139078/
- ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXoypizjW3WknFiJnKLwHCnL72vedxjQkDDP1mXWo6uco/wiki/Interstitial_fluid.html
- opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiology/chapter/26-1-body-fluids-and-fluid-compartments/
- www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-edema-in-adults
- www.elsevier.com/books/robbins-and-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease/kumar/978-1-4557-2613-
- www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20366493
- study.com/academy/lesson/anasarca-definition-causes-treatment.html#lesson
- A common side effect of antihypertensive therapy. Curr Cardiol Rep 2002; 4(6):479
- www.uptodate.com/contents/image?imageKey=PC%2F53550&topicKey=PC%2F6878&search=anasarca&rank=1~59&source=see_link
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anasarca
- drugsdetails.com/anasarca-definition-pictures-causes-and-treatment/
- O’Brien JG, et al. (2005). www.aafp.org/afp/2005/0601/p2111.html
- Semb KA, et al. (1998).www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9779722
- Şener D, et al. (2005). www.journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1345/aph.1E410
- Fauci AS, et al. Harrison’s Manual of Medicine 17th edition. McGraw-Hill Medical. 2009
- Medicalopedia. Available from: http://medicalopedia.org/3092/anasarca/



